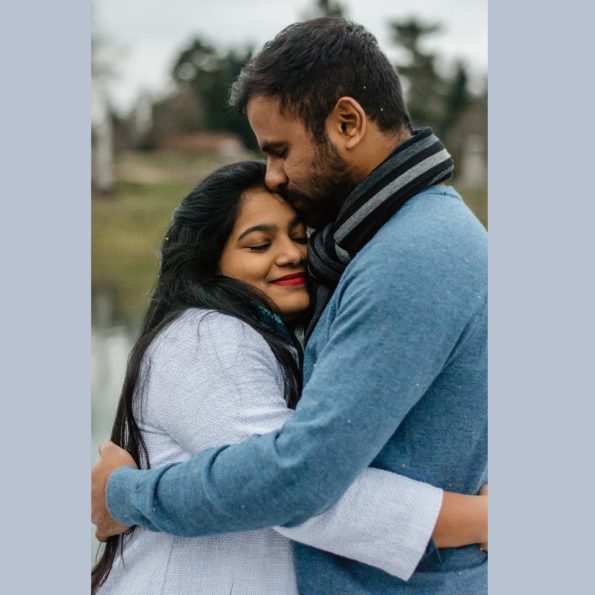
Women instructed to embrace their romantic partner prior to undergoing a stressful experience had a lower biological stress response—as indicated by levels of the stress hormone cortisol in saliva—compared to women who did not embrace their partner.
This effect was not seen for men.
In some settings, social touch may buffer against stress. Previous research has shown that massages, embraces combined with hand-holding, and embraces combined with affectionate communication can all reduce signs of stress in women. However, few studies have investigated these effects in men and it didn’t turn out like that of the ladies.
To explore potential stress-reducing effects of embracing, Berretz and colleagues conducted an analysis of 76 people in romantic relationships. All participants underwent a stress-inducing test in which they were asked to keep one hand in an ice-water bath for three minutes while being observed and maintaining eye contact with a camera.
Prior to this test, half of the couples were instructed to embrace, and the others did not embrace. The researchers measured various indicators of stress, including participants’ salivary cortisol levels, before and after the experiment.
Statistical analysis revealed that women who embraced their partners had a lower cortisol response to the stress test than women who did not embrace their partners.
However, for men, no associations were observed between embrace and stress-induced cortisol response. Other measures of stress including changes in blood pressure and emotional state did not show any associations with partner embrace.
These results suggest that a brief embrace with a romantic partner might subsequently reduce the cortisol response for women facing stressful social situations, such as school exams, job interviews, or presentations.
Further research could investigate whether this benefit extends to embraces with platonic friends.
The authors also call for research into related effects of the COVID-19 pandemic. Such investigations could explore whether social restrictions that reduced social touch may be associated with observed increases in stress and depression during the pandemic.
The authors add, “As a woman, hugging your romantic partner can prevent the acute stress response of your body.”
Originally from: https://medicalxpress.com/news/2022-05-women-partner-subsequently-stress-induced-cortisol.html