Eggplants are known by various names in different countries around the world. In the U.K., eggplants are called aubergines, while in Germany, they’re called eierfrucht. While eggplants are fixtures in the American marketplace, their production is highly concentrated in seven countries. These include China, India, Egypt, Turkey, and Japan.
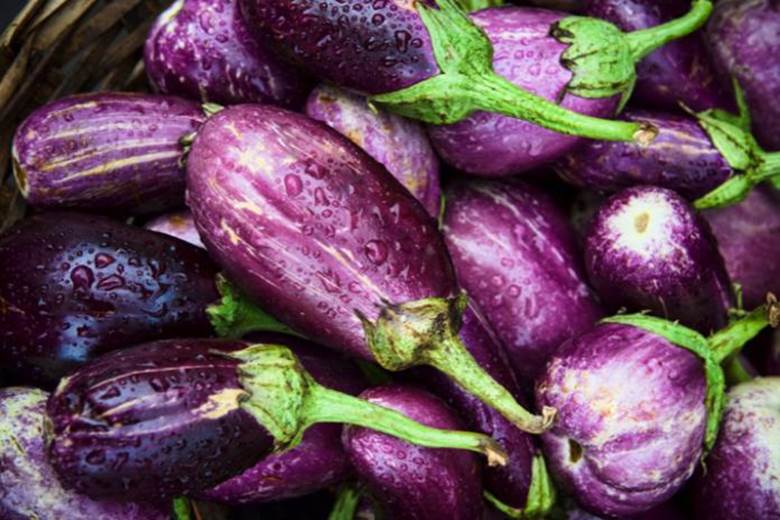
It contains many small seeds and grows from the edible flower of the Solanum melongen plant. One eggplant type is small, white and looks a lot like an egg; another is long and skinny like a bean, while the “Toga” variety is yellow-orange with green stripes. What they all have in common, however, is the way they grow, suspended from tall plants that can reach up to 1.5 meters in height.
One interesting aspect of eggplant is that it’s a member of the nightshade family of plants, along with tomatoes, potatoes and bell peppers, as well as chili peppers, habaneros, jalapenos and paprika.
As a member of the nightshade family, eggplants contain high levels of lectins, which are sugar-binding proteins that function as a defense mechanism for plants. These proteins are known to cause long-term health problems in humans, specifically targeting metabolism, cellular health, and endocrine function. Their pro-inflammatory effects may also heighten your risk of heart disease and cancer. While eggplants offer numerous health benefits, they should be eaten in moderation, along with legumes and other foods high in lectins.
Health benefits Meet the eggplant
Meet the eggplant
It contains a somewhat rare and extremely beneficial type of antioxidant known as nasunin. Nasunin is a type of anthocyanin antioxidant found in all types of eggplant varieties, in addition to other deeply colored fruits and vegetables. Nasunin is one of the key contributors to the health benefits of eggplant nutrition. Like other antioxidants, it has the ability to fight free radical damage in the body, which is often the cause of disease development and the mechanism at which our bodies age.
Most of the nasunin present within this veggie/fruit is found in its purple skin, so consuming the entire vegetable, including its peel, is important to reap all the health benefits. It also contains a high amount of antioxidants, special phytonutrients, including phenolic compounds, flavonoids, and numerous vitamins and minerals too. And all of these eggplant nutrition benefits come at a low-calorie count of only 35 calories per cup, thanks to its high fiber and water content.
Eggplant Nutrition Facts
One cup (about 82 grams) of raw eggplant nutrition contains approximately:
- 19.7 calories
- 4.7 carbohydrates
- 0.8 grams protein
- 0.2 grams fat
- 2.8 grams fiber
- 0.2 milligrams manganese (10 percent DV)
- 18 micrograms folate (5 percent DV)
- 189 milligrams potassium (5 percent DV)
- 2.9 micrograms vitamin K (4 percent DV)
- 1.8 milligrams vitamin C (3 percent DV)
- 0.5 milligrams niacin (3 percent DV)
- 0.1 milligrams vitamin B6 (3 percent DV)
- 11.5 milligrams magnesium (3 percent DV)
- 0.1 milligrams copper (3 percent DV)
Meanwhile, one cup (about 99 grams) of boiled eggplant nutrition contains approximately:
- 32.7 calories
- 9.1 grams carbohydrates
- 0.8 grams protein
- 0.2 grams fat
- 2.5 grams fiber
- 0.1 milligrams manganese (6 percent DV)
- 0.1 milligrams thiamine (5 percent DV)
- 2.9 micrograms vitamin K (4 percent DV)
- 0.1 milligrams vitamin B6 (4 percent DV)
- 0.6 milligrams niacin (3 percent DV)
- 13.9 micrograms folate (3 percent DV)
- 10.9 milligrams magnesium (3 percent DV)
- 122 milligrams potassium (3 percent DV)
- 0.1 milligrams copper (3 percent DV)
Types
 Eggplant
Eggplant
Some types of eggplant varieties include:
 Health benefits of Eating Garden Eggplant – 9jafoods
Health benefits of Eating Garden Eggplant – 9jafoods
- African garden egg
- Japanese eggplant/Chinese eggplant
- Western or globe
- Graffiti/Sicilian eggplant
- Italian eggplant
- White eggplant
- Indian eggplant
- Little green eggplant
- Thai eggplant
- Black magic
- Black beauty
- Little fingers
- Ichiban
- Slim Jim
The health benefits of eggplant nutrition seem to be consistent across the different types, with the exception of the variety known as “black magic” eggplant. This strand, which is sold commercially in U.S. markets, is known to have the highest concentration of certain phytonutrients and may offer additional antioxidant properties not found in other types.
Some sources have found that black magic eggplants can have up to three times the amount of antioxidant phenolics as the other types, although more research is needed to confirm the exact differences.
Scientific Studies on Health benefits
Has Anti-Inflammatory and Antioxidant Effects
The most studied eggplant health benefits is the antioxidant content. One study by Noda et al 1998. demonstrates that, nasunin is a potent fighter of inflammation and oxidative stress, acting as an O2 scavenger and an iron “chelator,” which can protect against lipid peroxidation. It is used to help iron become absorbable by the body and bind molecules to poisonous metal agents, such as mercury, arsenic, and lead, which can then be carried out of the body, resulting in a detox.
The same researchers in 2000 further published another animal study from Toxicology and found that nasunin, is a potent antioxidant that fights free radicals and protects the lipids (fats) in brain cell membranes from damage.
Another 2010 study conducted by Akanitapichat et al which analyzed Five eggplant varieties for their phenolic and flavonoid content, and their effect on cytotoxicity in liver cells. The researchers found that there was a significant correlation between flavonoids and hepatoprotective activities.
Kimural et al 1999 study also demonstrates that Nasunin defends against DNA and cell membrane damage caused by oxidative stress, as it has positive effects on cell walls. A recent 2019 study by Sukprasansap et al conducted also proved that Nasunin has the ability to protect the fat (or lipid) layer of the cell membrane that keeps its structure intact and prevents mutation or cell death.
Nasunin is one antioxidant involved in the ability to help cells receive and use nutrients from food and to discard waste. Without enough antioxidants like nasunin present within the body, toxins, and waste build up and can lead to a host of diseases, including cancer, heart disease, arthritis, and more.
Helps Protect Against Cancer
According to Jillian Levy, 2019, there are 13 types of protective phenolic acids present at significant levels within eggplant. “Different types of eggplants have varying levels of antioxidants and phytonutrients, but all share similar qualities in their ability to fight cancer ”.
Eggplant nutrition contains disease-fighting nasunin, as previously mentioned, in addition to many other phytonutrients, like chlorogenic acid. Chlorogenic acid is a type of polyphenol that has been linked with benefits such as regulation of glucose and lipid metabolism.
Chlorogenic acid is found in the cell walls of certain plants and known to be very beneficial in stopping free radicals from forming cancerous cells and leading to cancer tumor growth. In addition to its anti-mutagen and anti-tumor effects, chlorogenic acid is believed to act as an antimicrobial, anti-LDL (bad cholesterol), and antiviral, meaning it protects against various levels of inflammation and disease formation.
Helps Lower High Cholesterol and Blood Pressure
A 2018 study conducted by Yamaguchi et al shows that eggplant has anti-hypertensive effects and can be beneficial for heart health due to its ability to fight inflammation and oxidative stress. This leads to healthier arteries, more balanced cholesterol levels, and blood pressure that remains in the normal range.
Eggplant nutrition has been shown to be beneficial in maintaining healthy normal cholesterol levels because of its phytonutrients’ ability to improve circulation and reduce plaque buildup in the main arteries, including the aorta. While your body does need a certain amount of cholesterol, consuming eggplant is correlated with balancing the amount that is held within your blood vessel walls and improving blood flow.
Also, a 1998 study by Jorge et al aims to study the effect of eggplant on endothelium-dependent relaxation, and plasma lipids in hypercholesterolemic rabbits, and to assess the influence of this plant on the malondialdehyde (MDA) content of LDL particles and the arterial wall. The study concluded that hypercholesterolemic rabbits eggplant juice significantly reduced weight, plasma cholesterol levels, aortic cholesterol content.
Another research conducted by Das et al 2011 shows that eggplants containing potent cardio-protective compounds judging by their ability to increase left ventricular function (one of the main blood-pumping chambers of the heart) and reduce apoptosis.
Improve Digestive Health
The eggplant is mainly made up of water, which is why it is so low in calories. Eating vegetables that have a high content of water, fiber and nutrients helps flush out waste and toxins from the digestive tract. The digestive tract and colon need to be well-hydrated in order to push stool through the intestines and out of the body. Eating plenty of fresh, whole foods and drinking enough water is crucial for allowing the digestion system to expel toxins and excess water weight.
Because of the known benefits of eggplant nutrition, this veggie/fruit is included in the GAPS diet. GAPS is a diet especially helpful in correcting digestive disease, neurological issues, reducing inflammation and treating autoimmune diseases.
Because of the fiber and water content, it may be useful in helping achieve weight loss. It’s a great addition to any low-calorie, healthy diet because it provides an array of vital phytonutrients, vitamins and minerals yet are very low in calories.
Like other fruits/vegetables, it’s a source of mostly carbohydrates, but it also contains fiber — which means it can help make you feel full, so you are less likely to overeat. It’s extremely unlikely that eating too much eggplant would lead to weight gain, unless of course, you eat lots of high-calorie eggplant parmesan or other eggplant recipes that are rich in cheese, oil, etc.
Source of Bone-Building Manganese
According to Jillian Levy, 2019, Something you may not already know about eggplant nutrition is that one cup provides roughly 6 percent to 10 percent of your daily needs of important manganese. Manganese is a mineral that is naturally occurring in the body in small amounts, so the rest must be obtained from a healthy diet. It acts as an antioxidant, seeking out free radicals and eliminating them from causing bodily harm and oxidative stress. Manganese contributes to the formation of a healthy bone structure because of its impact on bone mineralization and metabolism. It is needed in order to metabolize and use calcium properly and to create essential enzymes for the formation of strong bones. Furthermore, manganese assists in the metabolic activity within the body, the formation of connective tissues and the regulation of hormone levels, which are crucial for reproductive health and fighting infertility. It also plays a part in regulating healthy thyroid gland function, fighting depression, and controlling blood sugar levels.
Good Source of Energy-Promoting B Vitamins
Also according to Jillian Levy, 2019, eggplant nutrition provides a good source of vitamin B1 and vitamin B6, two of the vitamins that are included in the healthy metabolism and energy-promoting B vitamin complex. B vitamins are water-soluble, found in many vegetables and other whole food sources, and are needed to maintain healthy energy levels, brain function, metabolism, heart health, and focus.
They are also required by the body to absorb all of the nutrients from the foods you eat, working to convert fats and carbohydrates into useable “fuel” for the body the burn. Vitamin B6 is needed to help create amino acids, which are the building blocks of proteins. Amino acids are used for numerous bodily functions, and without enough of them, problems including a lack of energy, skin inflammation, anemia, depression, chronic fatigue, and nutrient deficiencies can all occur.
Vitamin B6 is also involved in the formation of hemoglobin (which carries oxygen to the blood), neurotransmitters (which help control your mood), as well as regulation of blood glucose. Vitamin B1, meanwhile, is used to maintaining a healthy metabolism, blood and heart health, brain function, and more.
Help Prevent Skin Cancer
In one study by Cham et al 1991, when an extract is taken from the skin of an eggplant, a highly concentrated cream is made that studies have shown is able to help fight skin cancer. This type of cream contains a 10 percent concentration of solasodine rhamnosyl glycosides (BEC), which has been clinically proven as an effective treatment for several types of skin cancers: keratosis, basal cell carcinomas, and squamous cell carcinomas.
What are the side effects of eggplant?
It is one of the vegetables in the nightshade (Solanaceae) family. Other nightshade vegetables include tomatoes, bell peppers, and various types of potatoes. Nightshade vegetables are known for causing digestive disturbances in some people.
Eggplant and history of gout or kidney stones
Nightshade vegetables are high in oxalic acid, which has been correlated with an increased risk for forming kidney stones and arthritis in some people. For this reason, if you struggle with these conditions it may be best to try eliminating eggplant and other nightshade vegetables.
Can you eat too much eggplant?
Some people report feeling better after removing nightshade vegetables from their diets, suffering from less digestive distress and other inflammatory symptoms, including arthritis. However, there is more scientific evidence needed to prove this correlation still.
One study by Babu et al 1999 shows that eggplant does tend to be a common allergen for some people, and all types seem to have the same negative effects in those who react to negatively to this veggie/fruit due to allergies.
Summary
- eggplants are used as a traditional medicine in some Asian cultures, while others have utilized them for dishes such as eggplant parmesan and casseroles with other vegetables, cheese, meat and herbs
- Eggplant comes from the nightshade family of plants, which includes potatoes, tomatoes, and all kinds of peppers, though it has a somewhat controversial potential for adverse reactions after eating. However, in European and Middle Eastern cuisine, eggplant could be considered a delicacy, a tradition or perhaps a comfort food. As with any other food, it’s often all about the preparation.
- Eggplant nutrition is unique because this veggie (which is technically a fruit) contains antioxidants, including nasunin, phenolic compounds and anthocyanin.
- It is low in calories but provides fiber, some B vitamins, manganese, vitamin K and folate (especially when you eat more than one cup’s worth).
- Health benefits include providing antioxidants, fighting inflammation, offering protection against cancer, lowering cholesterol, improving digestion and protecting skin health.
- While it can be consumed raw, cooking it improves its taste, texture and nutrient availability.
- There are many options regarding how to cook this popular food. It can be grilled, baked, roasted, stuffed, sautéed or stir-fried.
DISCLAIMER This post is for enlightenment purposes only and should not be used as a replacement for professional diagnosis and treatments. Remember to always consult your healthcare provider before making any health-related decisions or for counselling, guidance and treatment about a specific medical condition.
The writer is an honorary Professor of Holistic Medicine-Vinnytsia State Pedagogical University, Ukraine and currently, LLB law/MBA Student. He is the formulator of FDA approved Nyarkotey Hibiscus Tea for Cardiovascular Support and wellness, Men’s Formula for Prostate Health and Women’s Formula for wellness. Contact: 0241083423/0541234556
References
- Noda Y, Kaneyuki T, Igarashi K, Mori A, Packer L. Antioxidant activity of nasunin, an anthocyanin in eggplant. Res Commun Mol Pathol Pharmacol. 1998;102(2):175‐187.
- Kimura Y, Araki Y, Takenaka A, Igarashi K. Protective effects of dietary nasunin on paraquat-induced oxidative stress in rats. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 1999;63(5):799‐804. doi:10.1271/bbb.63.799
- Sukprasansap M, Sridonpai P, Phiboonchaiyanan PP. Eggplant fruits protect against DNA damage and mutations. Mutat Res. 2019;813:39‐45. doi:10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2018.12.004
- Noda Y, Kneyuki T, Igarashi K, Mori A, Packer L. Antioxidant activity of nasunin, an anthocyanin in eggplant peels. Toxicology. 2000;148(2-3):119‐123. doi:10.1016/s0300-483x(00)00202-x
- Pannarat Akanitapichat , Kallayanee Phraibung , Kwunchai Nuchklang , Suparichart Prompitakkul (2010) Antioxidant and hepatoprotective activities of five eggplant varieties. Food and Toxicology. Volume 48, Issue 10 , October 2010, Pages 3017-3021
- Yamaguchi S, Matsumoto K, Koyama M, et al. Antihypertensive effects of orally administered eggplant (Solanum melongena) rich in acetylcholine on spontaneously hypertensive rats. Food Chem. 2019;276:376‐382. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.10.017
- Jorge PA, Neyra LC, Osaki RM, de Almeida E, Bragagnolo N. Efeito da berinjela sobre os lípides plasmáticos, a peroxidação lipídica e a reversão da disfunção endotelial na hipercolesterolemia experimental [Effect of eggplant on plasma lipid levels, lipidic peroxidation and reversion of endothelial dysfunction in experimental hypercholesterolemia]. Arq Bras Cardiol. 1998;70(2):87‐91. doi:10.1590/s0066-782×1998000200004
- Das S, Raychaudhuri U, Falchi M, Bertelli A, Braga PC, Das DK. Cardioprotective properties of raw and cooked eggplant (Solanum melongena L). Food Funct. 2011;2(7):395‐399. doi:10.1039/c1fo10048c
- Cham BE, Daunter B, Evans RA. Topical treatment of malignant and premalignant skin lesions by very low concentrations of a standard mixture (BEC) of solasodine glycosides. Cancer Lett. 1991;59(3):183‐192. doi:10.1016/0304-3835(91)90140-d
- Babu BN, Venkatesh YP. Clinico-Immunological Analysis of Eggplant (Solanum melongena) Allergy Indicates Preponderance of Allergens in the Peel. World Allergy Organ J. 2009;2(9):192‐200. doi:10.1097/WOX.0b013e3181b71c07

Raphael Nyarkotey Obu, PhD, © 2020
Prof Raphael Nyarkotey Obu is an honorary professor of holistic medicine-Vinnytsia State Pedagogical University, Ukraine and the President of Nyarkotey College of Holistic Medicine, Tema Community 7, Post office.Column: RaphaelNyarkoteyObu